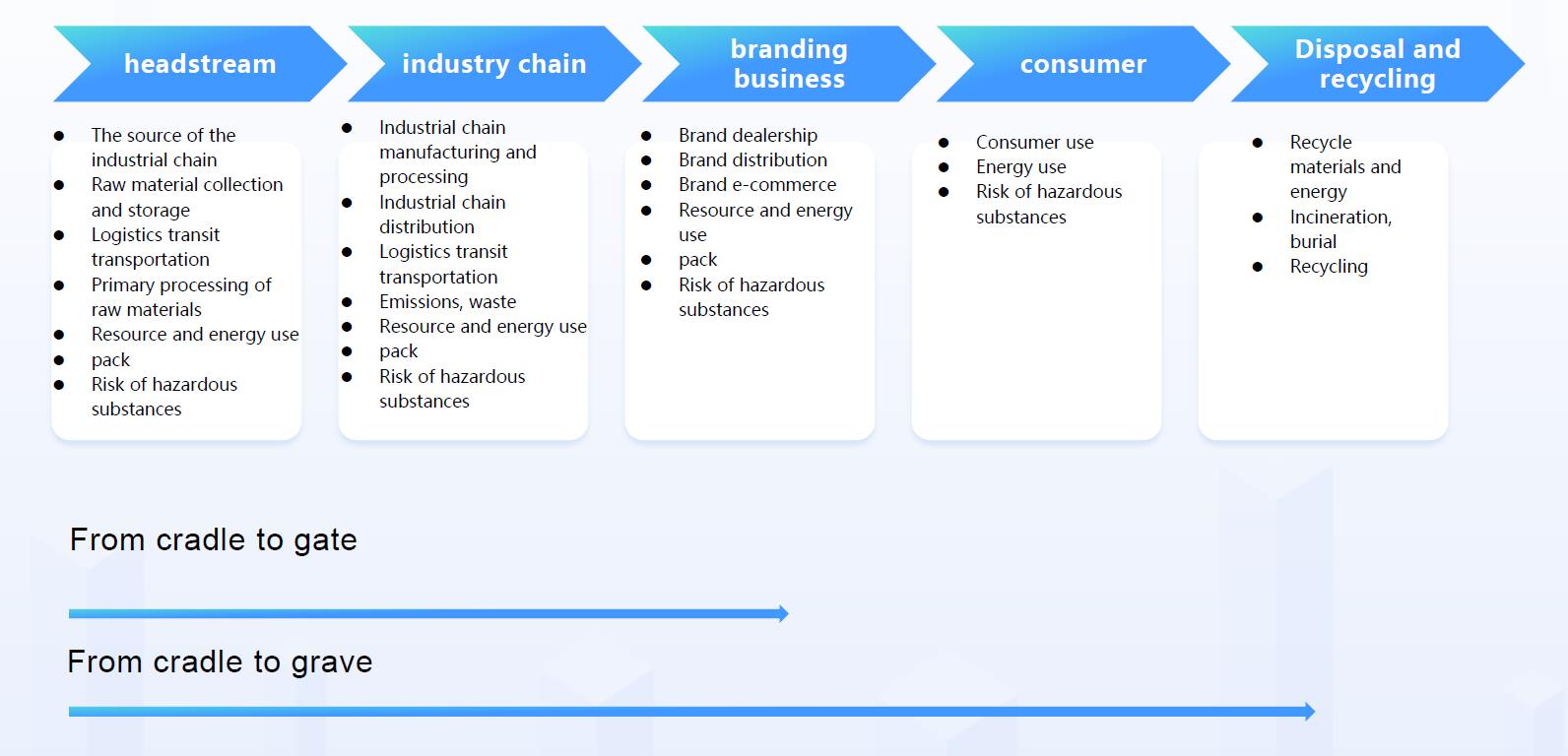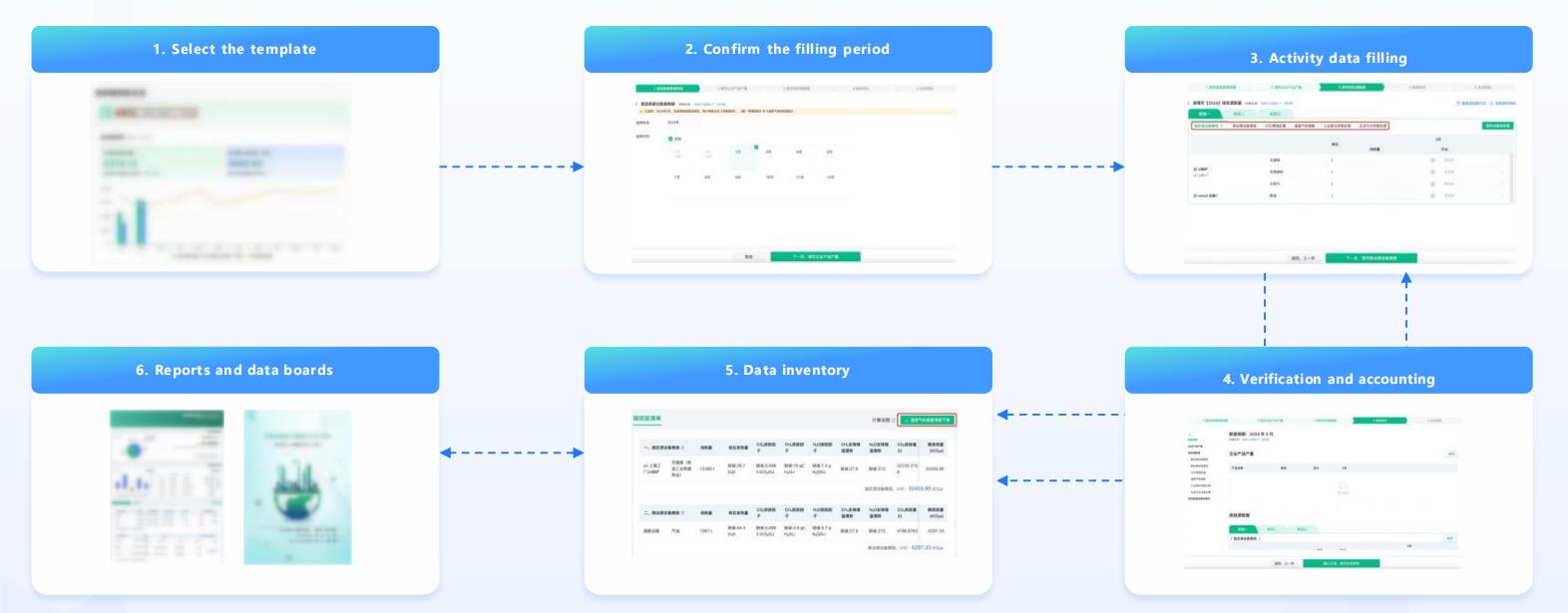
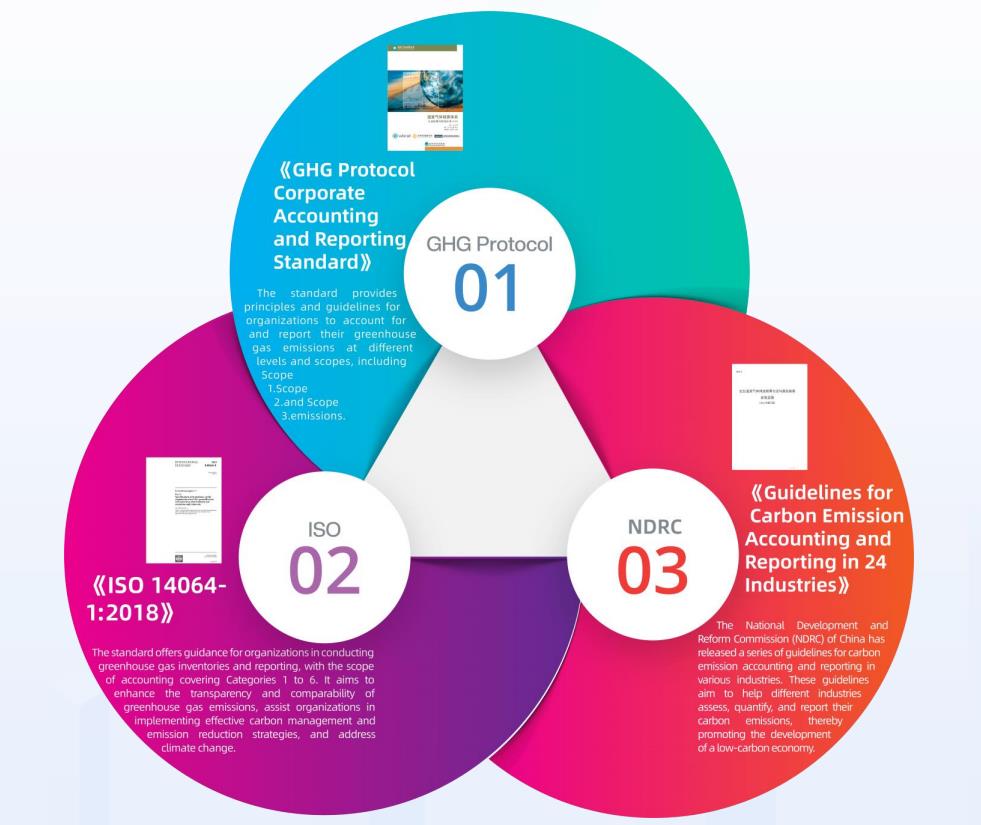
Amid increasing global pressure for sustainability, organizations are rapidly adopting carbon emission accounting systems and product carbon footprint (PCF) management platforms. Major retailers like JD.com, TMAIL, Suning, and Amazon have seen significant consumer engagement with energy-efficient products, highlighting a shift toward greener consumption. At the same time, international green trade policies such as the EU’s CBAM and the U.S. Clean Competition Act are intensifying the urgency for export-oriented enterprises to adapt, making carbon footprint transparency a critical factor for global competitiveness.
Industry leaders—including Tesla, Apple, GE, Schneider, Siemens, and IKEA—are spearheading value chain carbon neutrality by 2030, demanding upstream suppliers provide certified carbon footprint data. Meanwhile, ESG disclosure obligations are growing more stringent for publicly listed companies, with low-carbon strategies becoming central to investment evaluations and brand positioning. As a result, PCF accounting is emerging as a vital tool for value enhancement, regulatory compliance, and driving sustainable growth across the full product lifecycle.
JD.com: In 2021, the transaction value of household appliances with second-level or higher energy efficiency on JD.com accounted for over 6.5%. TMAIL: During the 2021 Double 9 shopping festival, TMAIL’s green home appliance section sold over 500,000 units of national first-level energy efficiency appliances. Sunings: In 2021, the number of people participating in trade-in programs across all channels on Sunings increased by 74%. Sales of first-level energy efficiency air conditioners grew by 69%, and sales of smart home products increased by 68%. Amazon: Launched a CPF product section and related recommendations, with a 70% increase in product click-through rates in 2021.
The European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) and the EU’s New Battery Law have been introduced successively. Meanwhile, the U.S. Clean Competition Act (CCA) draft is under development. Europe, South Korea, and the United States have also set requirements for the carbon footprint of photovoltaic modules. Green trade barriers are accelerating the formation, and export-oriented companies are compelled to respond.
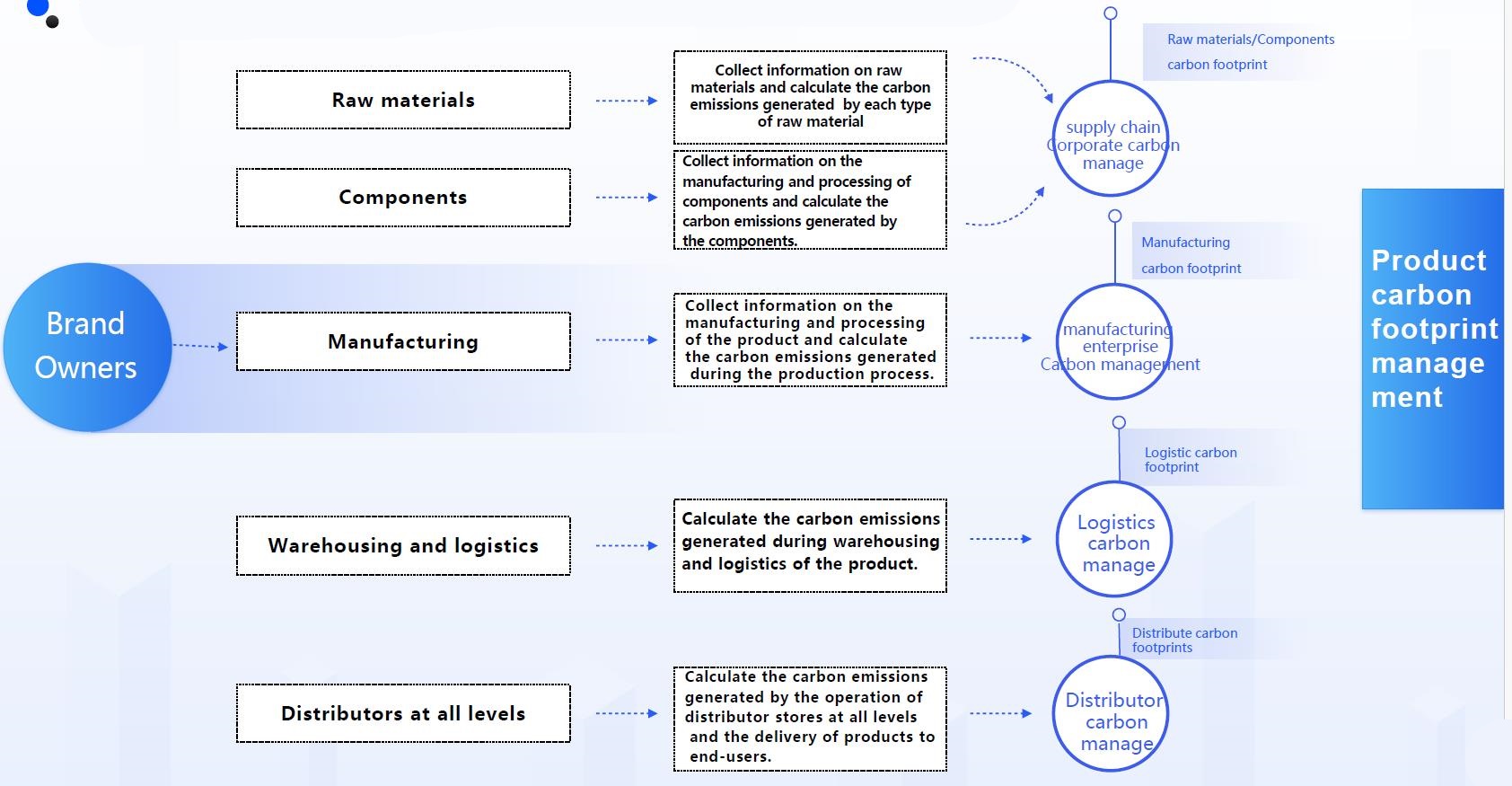
Leading companies in the automotive, 3C, electrical, retail and other industries (Tesla, Apple, GE, Schneider, Siemens, KEA, etc.) have proposed the goal of achieving carbon neutrality in the whole value chain by 2030, and then calculate and control the carbon footprint of raw materials and components provided by upstream suppliers, and provide effective carbon footprint certificates.
Leading companies in industries such as automotive, 3C, electrical, and retail (including Tesla, Apple, General Electric, Schneider, Siemens, and IKEA) have set a goal to achieve full value chain carbon neutrality by 2030. To this end, they are calculating and managing the carbon footprints of raw materials component provided by upstream suppliers and are also issuing valid carbon footprint certificates.
ESG Disclosure Requirements for Listed Companies: Companies listed on their own scope and technology and other overseas exchanges are increasingly required to disclose ESG information. Low-carbon products and services are an important component of ESG. Investor Requirements in ESG: For example, Security and Consultors a company’s ESG and carbon management capabilities at key indicators and has established a corresponding evaluation system. Corporate ESG Promotion Needs: Companies promote their products and services through their utility websites and other media, aiming to track the industry and change market value. This approach has led to a 30% increase in market value and a 30% growth in new customer order rates.